The Importance of Iodine for Optimal Thyroid Function

What is Iodine and Why is it Important?
Iodine is a trace element that plays a vital role in human health, particularly for the thyroid gland. This small but mighty nutrient is essential for the production of thyroid hormones, which regulate metabolism, energy levels, and overall growth. Without adequate iodine, the body struggles to produce these hormones, leading to various health issues.
Iodine is the most important mineral for the thyroid, and it is essential for all aspects of health.
The thyroid gland, a butterfly-shaped organ located in the neck, requires iodine to synthesize thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). These hormones influence almost every cell in the body, affecting everything from heart rate to digestion. Thus, iodine isn't just important; it's fundamental for our body's functioning.
Moreover, iodine deficiency can lead to conditions such as goiter, hypothyroidism, and even developmental issues in children. Ensuring we get enough iodine through diet or supplements is crucial, especially in areas where iodine levels in soil and food are low.
How Iodine Affects Thyroid Hormone Production
The process of thyroid hormone production begins when iodine is absorbed from the diet and transported to the thyroid gland. Inside the gland, iodine combines with the amino acid tyrosine to create T4 and T3. This intricate process underscores the importance of having sufficient iodine in our diets, as a lack of it can lead to imbalances.
When iodine levels are low, the thyroid gland may enlarge, trying to capture more iodine from the bloodstream, which leads to goiter. This compensatory mechanism is nature's way of safeguarding hormone production, but it can result in visible and uncomfortable symptoms. Without intervention, this can spiral into more severe thyroid disorders.
Iodine is vital for thyroid health
Iodine is essential for the production of thyroid hormones that regulate metabolism and overall growth.
Conversely, when iodine intake is adequate, the thyroid can function optimally, producing the right amount of hormones needed for energy regulation and metabolic balance. This highlights the delicate balance the body maintains and the significant role iodine plays in ensuring our thyroids work efficiently.
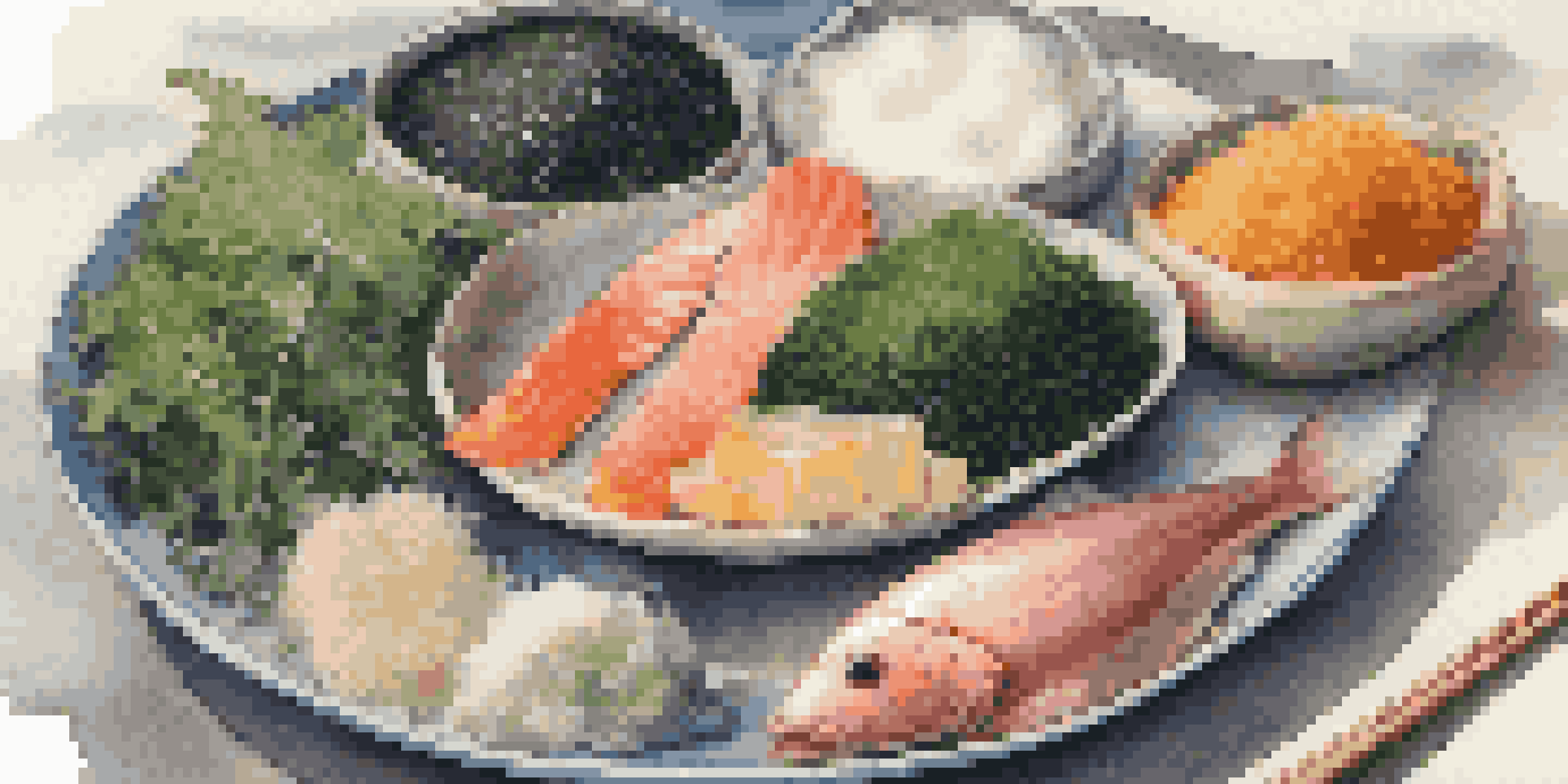
Sources of Iodine in Our Diet
Iodine can be found in various foods, making it relatively easy to include in our diet. Sea vegetables like kelp and nori are particularly rich in iodine, offering a natural source for those looking to enhance their intake. Additionally, iodized salt is a common household staple that has been fortified to combat iodine deficiency.
The thyroid is a master gland, and iodine is a key component in maintaining its health.
Other dietary sources include dairy products, eggs, and certain fish such as cod and tuna. For vegetarians or those with dietary restrictions, iodine can also be obtained from fortified foods and supplements. It's essential to be mindful of your iodine intake, especially if your diet lacks these iodine-rich foods.
However, it's important to strike a balance; too much iodine can also lead to thyroid dysfunction. The key is to aim for sufficient intake without overdoing it, ensuring your thyroid remains happy and healthy.
Iodine Deficiency: Causes and Consequences
Iodine deficiency can occur for several reasons, including a diet low in iodine-rich foods, certain health conditions, or geographic factors where soil lacks iodine. This deficiency can lead to serious health issues, particularly in pregnant women and young children, as it can affect fetal development and cognitive function.
The consequences of iodine deficiency can manifest as goiter, hypothyroidism, or even developmental delays in children. In severe cases, it can lead to cretinism, a condition marked by stunted physical and mental growth. These potential outcomes highlight the importance of addressing iodine deficiency proactively.
Deficiency leads to serious issues
Iodine deficiency can result in conditions such as goiter and developmental delays, particularly in children and pregnant women.
Public health initiatives, such as iodization of salt, have significantly reduced the prevalence of iodine deficiency in many parts of the world. However, awareness and education on this topic remain crucial to prevent resurgence and ensure everyone has access to adequate iodine.
Symptoms of Iodine Deficiency
Recognizing the symptoms of iodine deficiency is essential for early intervention. Common signs include fatigue, weight gain, sensitivity to cold, and dry skin, all of which can stem from an underactive thyroid. In some cases, individuals may also experience hair loss or a noticeable swelling at the base of the neck due to goiter.
In children, iodine deficiency can lead to cognitive impairments, learning difficulties, and stunted growth, making it crucial for parents to monitor dietary intake. If you or someone you know exhibits these symptoms, it might be worth exploring iodine levels with a healthcare professional.
Being proactive about iodine intake can help mitigate these symptoms and foster better overall health. Simple dietary adjustments or consulting a nutritionist can provide the guidance needed to ensure you’re getting enough of this vital nutrient.
The Role of Iodine in Pregnancy
Iodine is particularly crucial during pregnancy, as it supports the developing fetus’s brain and neurological system. Pregnant women require about 220 micrograms of iodine daily, which is significantly more than the standard recommendation for adults. This increase underscores the importance of monitoring iodine intake during this critical period.
Adequate iodine levels can help prevent complications such as cretinism and developmental delays in newborns. Health professionals often recommend iodine supplements for pregnant women, especially if dietary sources are insufficient. It’s vital for expectant mothers to consult with their healthcare providers to ensure they meet their iodine needs.
Diet and supplements ensure intake
Incorporating iodine-rich foods and supplements is crucial for maintaining adequate levels and supporting thyroid function.
Furthermore, breastfeeding mothers also need to pay attention to their iodine intake, as it not only aids their health but ensures their infants receive the necessary iodine through breast milk. Ensuring adequate iodine levels during these early stages can have lasting positive effects on a child's development.
Conclusion: Prioritizing Iodine for Thyroid Health
In conclusion, iodine is a small yet essential element that plays a significant role in maintaining optimal thyroid function. Its impact on hormone production, metabolism, and overall well-being cannot be overstated. By ensuring adequate iodine intake, we can support our thyroid health and avoid the pitfalls of deficiency.
Whether through diet, supplements, or iodized salt, finding ways to incorporate iodine into your daily routine is crucial. If you're unsure about your iodine levels, consider consulting a healthcare professional for personalized advice. Taking these steps can provide peace of mind and help you feel your best.

Remember, a healthy thyroid contributes to a healthy life. By prioritizing iodine, you’re investing in your health, energy levels, and overall quality of life.