The Biopsychosocial Model of Health Explained
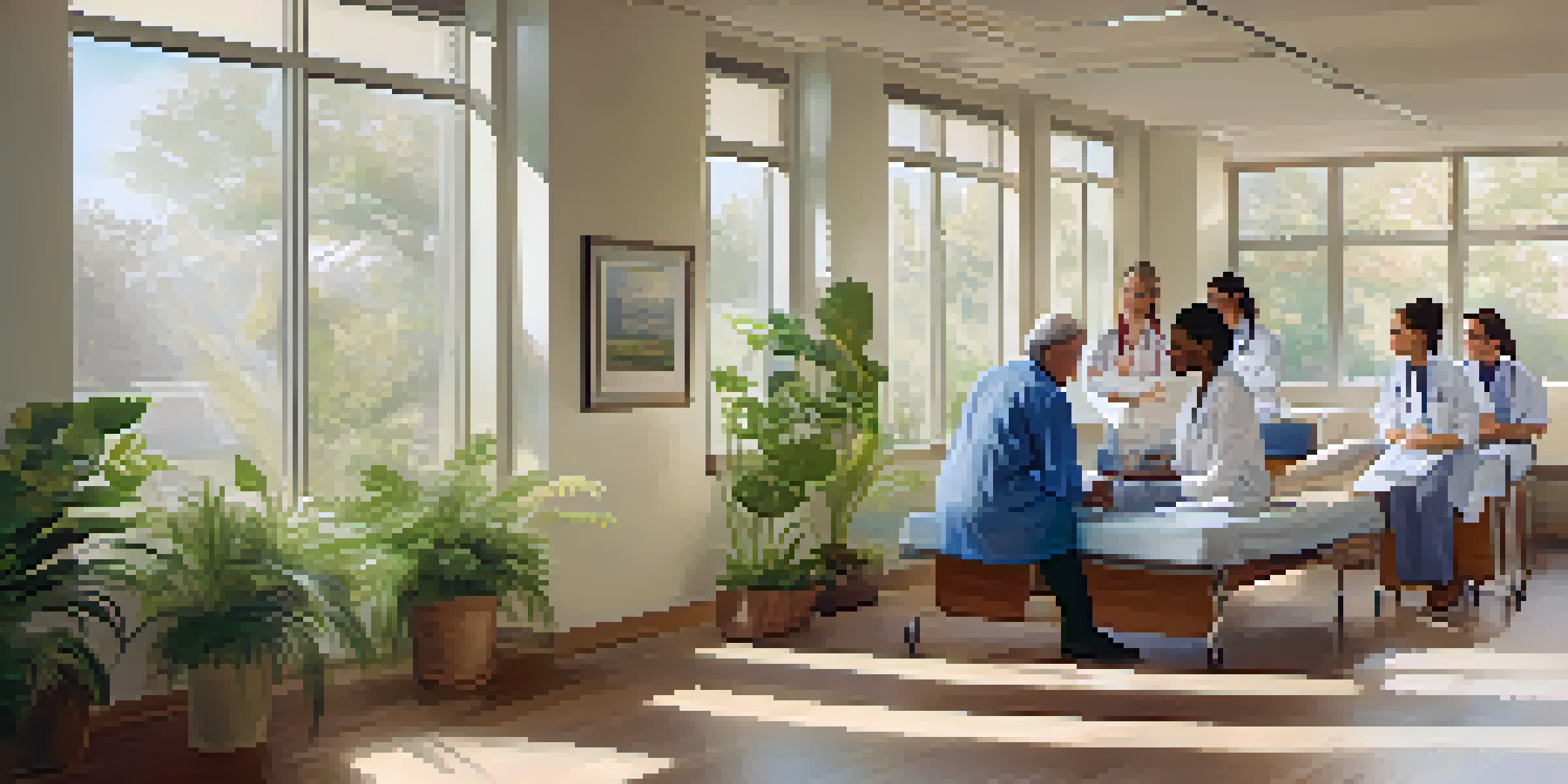

What Is the Biopsychosocial Model of Health?
The biopsychosocial model of health is an approach that considers biological, psychological, and social factors in health and illness. Unlike traditional models that focus solely on the physical aspects, this comprehensive framework emphasizes the interplay of various elements that contribute to a person's overall well-being. By acknowledging the complexity of human health, the biopsychosocial model provides a more holistic perspective.
Health is not merely the absence of disease. It is a state of complete physical, mental, and social well-being.
For example, when a person experiences chronic pain, the model suggests looking beyond just the physical source of pain. Psychological factors, such as stress or anxiety, and social influences, like family support or work environment, can also play critical roles in how that individual perceives and manages their pain. This multifaceted approach allows healthcare providers to tailor interventions that address the unique needs of each patient.
In essence, the biopsychosocial model serves as a reminder that health is not just the absence of disease but a dynamic state influenced by a variety of interconnected factors. Emphasizing this complexity can lead to better patient outcomes and a deeper understanding of what it means to be healthy.
The Biological Component: Understanding the Basics
The biological component of the biopsychosocial model focuses on the physical aspects of health, including genetics, biochemical processes, and bodily functions. This includes everything from how our immune system operates to how our genes may predispose us to certain health conditions. Understanding these biological factors is crucial in diagnosing and treating illnesses.
For instance, consider someone with a family history of heart disease. Their biological risk factors, like high cholesterol or hypertension, can significantly influence their health outcomes. By recognizing these risks, healthcare providers can implement preventive measures, such as lifestyle changes or medications, to mitigate potential issues.
Holistic Health Approach Explained
The biopsychosocial model integrates biological, psychological, and social factors to provide a comprehensive understanding of health and illness.
Ultimately, the biological component serves as the foundation of the biopsychosocial model, illustrating that while our physical health is vital, it does not exist in isolation. Instead, it interacts with psychological and social factors, shaping our overall health experience.
The Psychological Component: Mind Matters
The psychological component examines how mental processes and emotional states impact health. This includes factors like stress, coping mechanisms, and mental health conditions such as depression or anxiety. Our thoughts and feelings can significantly influence physical health, which is why addressing psychological factors is essential in the biopsychosocial model.
The greatest weapon against stress is our ability to choose one thought over another.
For example, consider a student preparing for exams. High levels of stress can lead to physical symptoms like headaches or fatigue, affecting their performance and overall health. By incorporating stress management techniques, such as mindfulness or relaxation exercises, the student can improve both their mental well-being and physical health.
In this way, the psychological component highlights the importance of mental health in the holistic assessment of a person's health. By fostering a positive mental state, individuals can enhance their resilience and overall quality of life.
The Social Component: Connecting with Others
The social component of the biopsychosocial model emphasizes the role of social interactions and support systems in health. Factors such as family dynamics, community support, and socioeconomic status can significantly influence a person's health outcomes. This aspect reminds us that we are not isolated beings but rather part of a larger social fabric.
For instance, a person recovering from surgery may heal more effectively if they have a supportive family or community. Emotional support can reduce feelings of isolation and promote a quicker recovery by encouraging positive behaviors, such as adhering to rehabilitation exercises. Conversely, social isolation can worsen health outcomes, demonstrating the critical nature of the social component.
Importance of Interconnectedness
The interplay between biological, psychological, and social components is crucial, as they influence one another and impact overall health outcomes.
By understanding the social dimensions of health, healthcare providers can develop interventions that foster social connections and support networks. This approach not only improves individual health but also strengthens community resilience.
Interplay Between Components: A Dynamic Relationship
One of the most compelling aspects of the biopsychosocial model is the interplay between its three components: biological, psychological, and social. These elements do not operate in silos; rather, they are interconnected and can influence one another in profound ways. Recognizing this dynamic relationship is key to understanding health and illness.
For example, an individual with a chronic illness may experience depression due to their condition, which can, in turn, affect their biological health by impacting their immune system. This cyclical relationship illustrates how addressing only one aspect of health may not yield the best results without considering the others. Interventions that target all three components often lead to more effective treatment.
By acknowledging this interplay, healthcare providers can adopt a more comprehensive approach to patient care, ultimately leading to improved health outcomes and a greater understanding of the complexities of human health.
Applications of the Biopsychosocial Model in Healthcare
The biopsychosocial model has practical applications in various healthcare settings, influencing how providers diagnose and treat patients. This approach encourages healthcare professionals to look beyond just the symptoms and consider the whole person. By adopting this model, providers can develop tailored treatment plans that address the unique needs of individuals.
For instance, in mental health care, therapists often utilize the biopsychosocial model to assess a client's situation holistically. They explore not only the client’s mental health symptoms but also their social environment and biological factors that may contribute to their condition. This comprehensive assessment can lead to more effective therapeutic strategies.
Future of Healthcare Practices
Advancements in technology and growing awareness of mental health and social determinants position the biopsychosocial model as vital for future healthcare integration.
Additionally, in chronic disease management, healthcare teams can collaborate across disciplines—medical doctors, psychologists, and social workers—to create a cohesive treatment plan that addresses all aspects of a patient's life. This integrative approach enhances patient engagement and promotes better health outcomes.
Challenges and Criticisms of the Biopsychosocial Model
While the biopsychosocial model offers a comprehensive framework for understanding health, it does face some challenges and criticisms. One concern is the difficulty in measuring and quantifying the social and psychological components, which are often subjective and variable. This can make it challenging for healthcare providers to implement the model consistently in clinical practice.
Critics also argue that the model may risk oversimplifying complex health issues by attempting to fit them into three distinct categories. Some health conditions may not neatly align with the biopsychosocial framework, leading to potential gaps in understanding. It's essential for practitioners to remain flexible and consider the unique context of each patient.

Despite these challenges, the biopsychosocial model remains a valuable tool in healthcare. By acknowledging its limitations and striving for a balanced approach, healthcare providers can continue to enhance their understanding of health and improve patient care.
The Future of the Biopsychosocial Model in Health
As our understanding of health continues to evolve, the biopsychosocial model is likely to play an increasingly important role in shaping healthcare practices. Advances in technology, such as telemedicine and health data analytics, provide new opportunities to integrate biological, psychological, and social factors more effectively. This integration can enhance patient care and promote holistic approaches to health.
Moreover, as society becomes more aware of mental health and social determinants of health, the biopsychosocial model offers a framework to address these critical issues. By prioritizing mental well-being and recognizing the impact of social influences, healthcare providers can foster a more inclusive and supportive environment for patients.
In conclusion, the future of the biopsychosocial model in health is promising. By continuing to embrace this holistic approach, we can work towards a healthcare system that recognizes the complexity of human health and promotes overall well-being.