Addressing Health Inequities Through Education
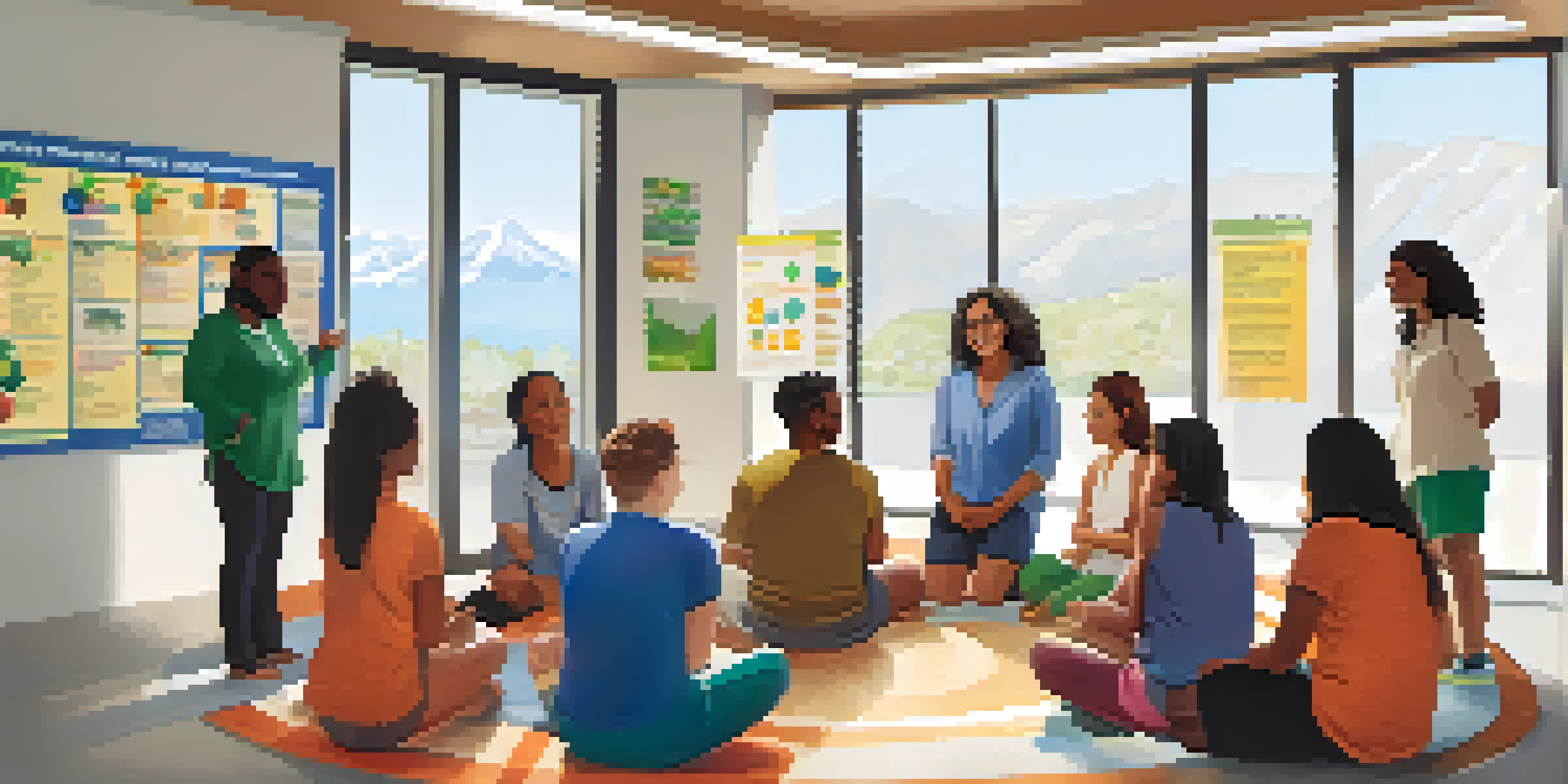

Understanding Health Inequities and Their Causes
Health inequities refer to the unfair and avoidable differences in health status among different population groups. These disparities often arise from social determinants of health, such as income, education, and geographic location. For instance, individuals living in low-income neighborhoods may lack access to quality healthcare and nutritious food, leading to poorer health outcomes.
Health is a human right, not a privilege to be purchased.
Moreover, systemic issues like racism and discrimination play a significant role in perpetuating these inequities. A person’s race or ethnicity can influence their access to healthcare services, resulting in higher rates of chronic diseases among marginalized communities. By understanding these root causes, we can better address the foundational issues that contribute to health disparities.
Recognizing the complexity of health inequities is the first step toward crafting effective educational strategies. Education can empower individuals to understand their health needs, navigate the healthcare system, and advocate for their rights, ultimately leading to improved health outcomes.
The Role of Education in Promoting Health Awareness
Education serves as a powerful tool in raising awareness about health issues and promoting healthier lifestyles. Schools and community programs can provide essential information on nutrition, exercise, and preventative care, enabling individuals to make informed choices. For example, a local health education workshop might teach families about the importance of a balanced diet, which could lead to better health practices within the community.
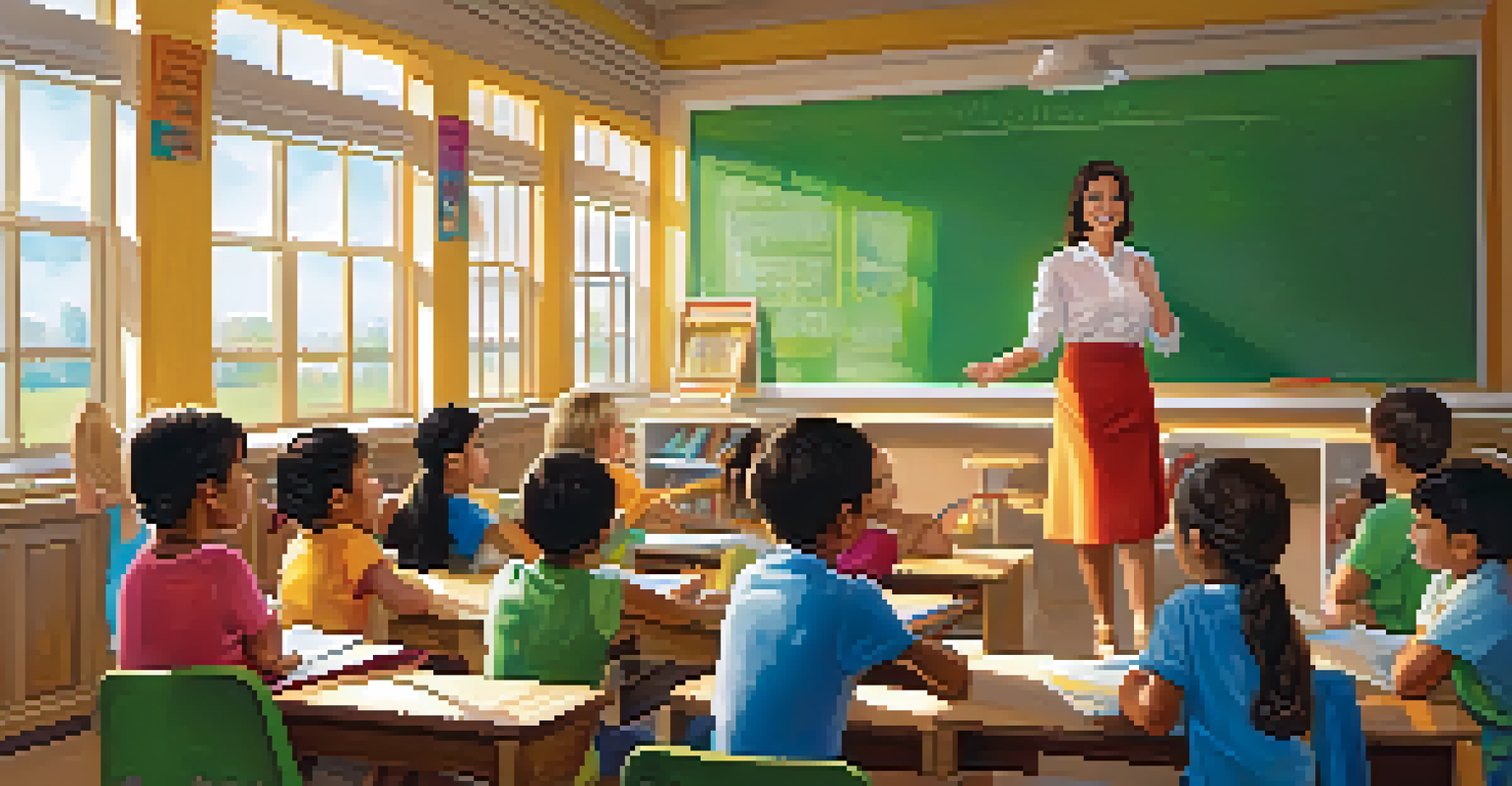

Additionally, educational initiatives can help demystify complex health information, making it accessible to everyone. When people understand health risks and the importance of regular check-ups, they are more likely to engage with healthcare services and seek preventive care. This proactive approach can significantly reduce the prevalence of chronic diseases in underserved populations.
Health Inequities Explained Simply
Health inequities are unfair differences in health status caused by social determinants like income and education.
Ultimately, by prioritizing health education, we can foster a culture of awareness that empowers individuals to take charge of their health. This shift not only benefits individuals but can also lead to healthier communities as a whole, reducing overall healthcare costs and improving quality of life.
Community-Based Programs: Bridging the Gap
Community-based programs play a crucial role in addressing health inequities through targeted education. These programs often tailor their approaches to meet the unique needs of specific populations, ensuring that health information is relevant and accessible. For instance, a community health center may offer workshops in multiple languages to cater to diverse populations, fostering inclusivity.
Education is the most powerful weapon which you can use to change the world.
Moreover, these programs can create supportive environments where individuals feel empowered to learn and share their experiences. By involving community members in the planning and implementation of health education initiatives, these programs can enhance trust and participation. The result is a more engaged community that is better equipped to tackle health challenges collectively.
Through collaboration with local organizations and stakeholders, community-based programs can amplify their impact. By pooling resources and expertise, these initiatives can develop comprehensive health education campaigns that resonate with the target audience, ultimately leading to improved health outcomes and reduced disparities.
The Importance of Culturally Competent Education
Culturally competent education recognizes and respects the diverse backgrounds of individuals and communities. This approach is vital in addressing health inequities, as it ensures that health messages resonate with the audience's cultural norms and values. For example, using culturally relevant examples in health education can facilitate better understanding and acceptance of important health information.
Additionally, culturally competent education promotes inclusivity and trust between healthcare providers and patients. When healthcare professionals are trained to understand cultural differences, they can communicate more effectively with patients, leading to improved patient satisfaction and adherence to treatment plans. This connection can make a significant difference in health outcomes, particularly for marginalized communities.
Education Empowers Health Choices
Educational initiatives raise awareness about health issues, enabling individuals to make informed decisions and improve their health.
By prioritizing culturally competent education in health initiatives, we can create an environment that values diversity and fosters better health communication. This approach not only benefits individuals but also strengthens community ties, promoting a collective effort toward achieving health equity.
Leveraging Technology to Enhance Health Education
In today’s digital age, technology plays a vital role in disseminating health information. Online platforms, social media, and mobile apps can be powerful tools for reaching a wide audience, particularly in underserved communities. For instance, a mobile app providing health tips in multiple languages can empower users to take control of their health from the comfort of their homes.
Moreover, technology can facilitate interactive learning experiences that engage individuals more effectively than traditional methods. Online webinars, virtual workshops, and health blogs can provide valuable information while allowing participants to ask questions and share their experiences. This level of engagement can enhance understanding and retention of critical health information.
As we continue to embrace technology in health education, it’s essential to ensure accessibility. Bridging the digital divide is crucial, as not everyone has equal access to the internet or digital devices. By addressing these barriers, we can maximize the benefits of technology in promoting health equity.
Policy Changes: Supporting Health Education Initiatives
Advocating for policy changes is essential for supporting health education initiatives that address health inequities. Policymakers have the power to allocate resources and funding for programs that prioritize education in underserved communities. For example, increasing funding for school-based health education programs can ensure that children receive crucial information about healthy habits from a young age.
Furthermore, policies that promote collaboration between educational institutions and healthcare organizations can enhance the effectiveness of health education initiatives. By creating partnerships, these entities can work together to design comprehensive programs that address the unique needs of their communities. This collaborative approach can lead to more sustainable and impactful health education efforts.
Community Programs Foster Inclusivity
Community-based programs address health inequities by tailoring education to meet the specific needs of diverse populations.
Ultimately, engaging in advocacy for policy changes can create a supportive environment for health education initiatives. When health education is prioritized at the policy level, it sends a clear message about the importance of addressing health inequities and empowers communities to take action.
Measuring Success: Evaluating Health Education Programs
To ensure the effectiveness of health education initiatives, it’s crucial to implement robust evaluation methods. By measuring outcomes, we can determine what works and what doesn’t, allowing for continuous improvement in program delivery. For instance, surveys and focus groups can provide valuable feedback from participants, helping to refine educational strategies.
Additionally, tracking health outcomes over time can help demonstrate the impact of health education on reducing inequities. For example, if a community program successfully increases awareness of preventive care, we might see a rise in routine check-ups and a decrease in chronic disease rates. These measurable results can bolster support for ongoing funding and resources.
Ultimately, evaluating health education programs is essential for accountability and transparency. By sharing success stories and lessons learned, we can inspire further investment in health education initiatives that work to address health inequities.